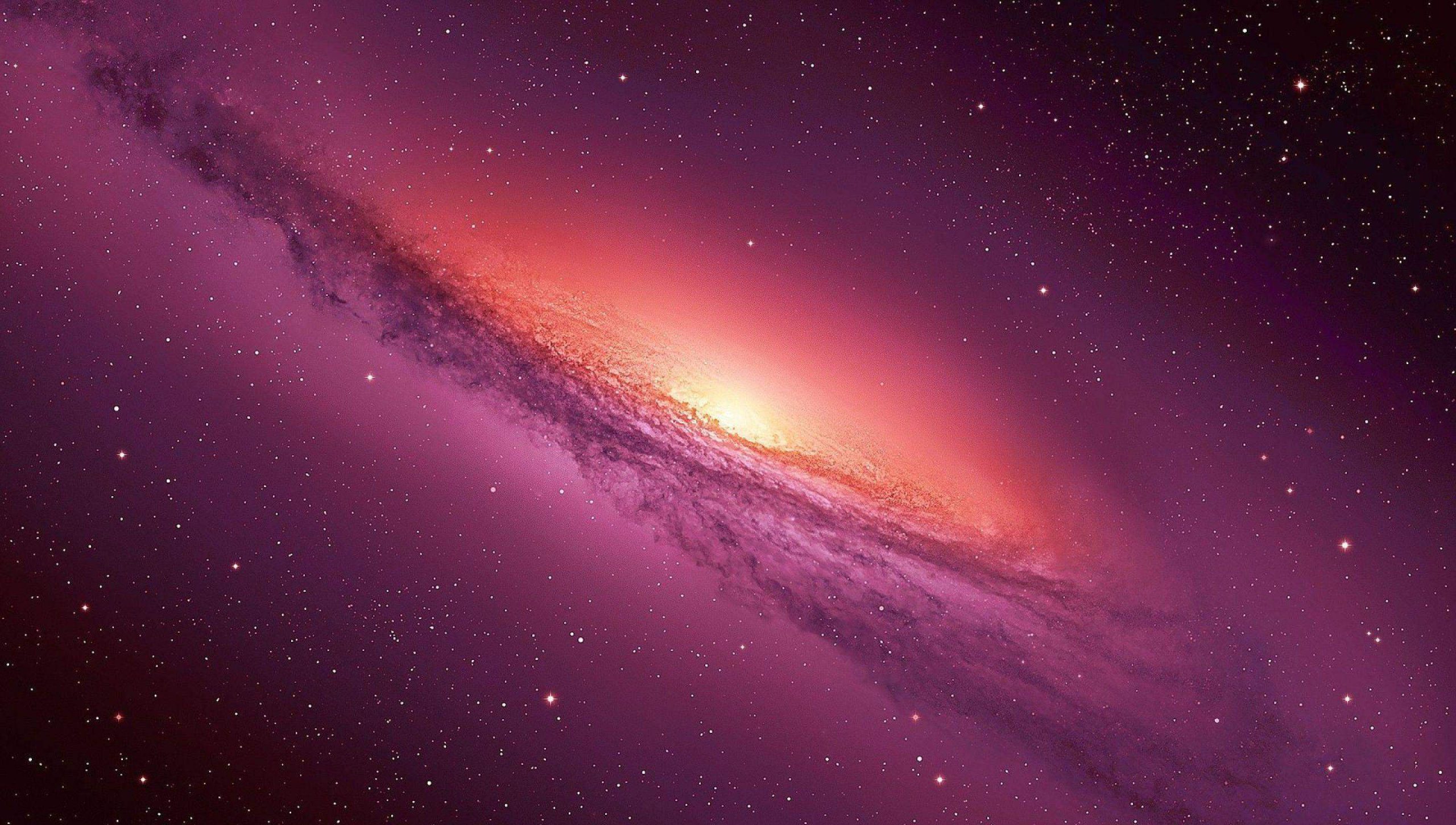

What Is A Galaxy?
A galaxy includes stars, gases, asteroids, planets, moons, and dust that are gathered together in a group by the gravitational force and are in a certain orbit.
The smallest galaxies are several hundred light-years across and consist of about 100 billion stars and The largest galaxies are up to 3 million light years across.
Today, more than 100 billion galaxies have been identified by astronomers, which have There are different types.
Types Of Galaxies:
Scientists classify galaxies based on their appearance using a method first proposed in 1925 by American astronomer Edwin Hubble.Hubble identified 3 main types of galaxies: spiral, elliptical, bar spiral.Irregular and dwarf galaxies are two types that were added later.
Elliptical galaxies:
In terms of shape, they vary from oval to spherical, and our shapes are found between these two. Unlike other galaxies, which reflect blue light from burning and short-lived stars, these galaxies appear yellow.
Spiral Galaxies:
They have arms that create a spiral shape around the central bulge or core, and the rotation of the core is accompanied by the rotation of the arms. The arms have a lot of dust and gas that leads to the formation of new stars.
Bar spiral Galaxies:
They have a central protruding nucleus and are rod-shaped. Some astronomers consider the Milky Way to be a barred spiral galaxy.
Irregular galaxies:
They have no regular shape and structure, and their mass is more than other galaxies, and most of the stars in them have a short life span and high brightness. About a quarter of the known galaxies are irregular.
Active galaxies:
All galaxies have a certain amount of electromagnetic radiation. Some galaxies abnormally emit a large amount of radiation. These galaxies are called active galaxies.
The energy of these galaxies comes from a source with a very large but dense mass located in the center of the galaxy.
Collision of galaxies:
Most of the galaxies are hundreds of thousands of light-years away from their neighboring galaxies, but still, some of them come close to each other to such an extent that their two-way gravity pulls the objects in other galaxies towards them.

Galaxies getting too close to each other may cause them to collide and then a radical change in the appearance of the galaxies.
Our Galaxy, The Milky Way:
Our beautiful galaxy, the Milky Way, is a spiral galaxy that contains billions of stars, planets, and black holes.
The planet we are in, along with our solar system, are part of this galaxy that is about 13.6 billion years old and is 100,000 light-years in diameter and only 1,000 light-years thick.
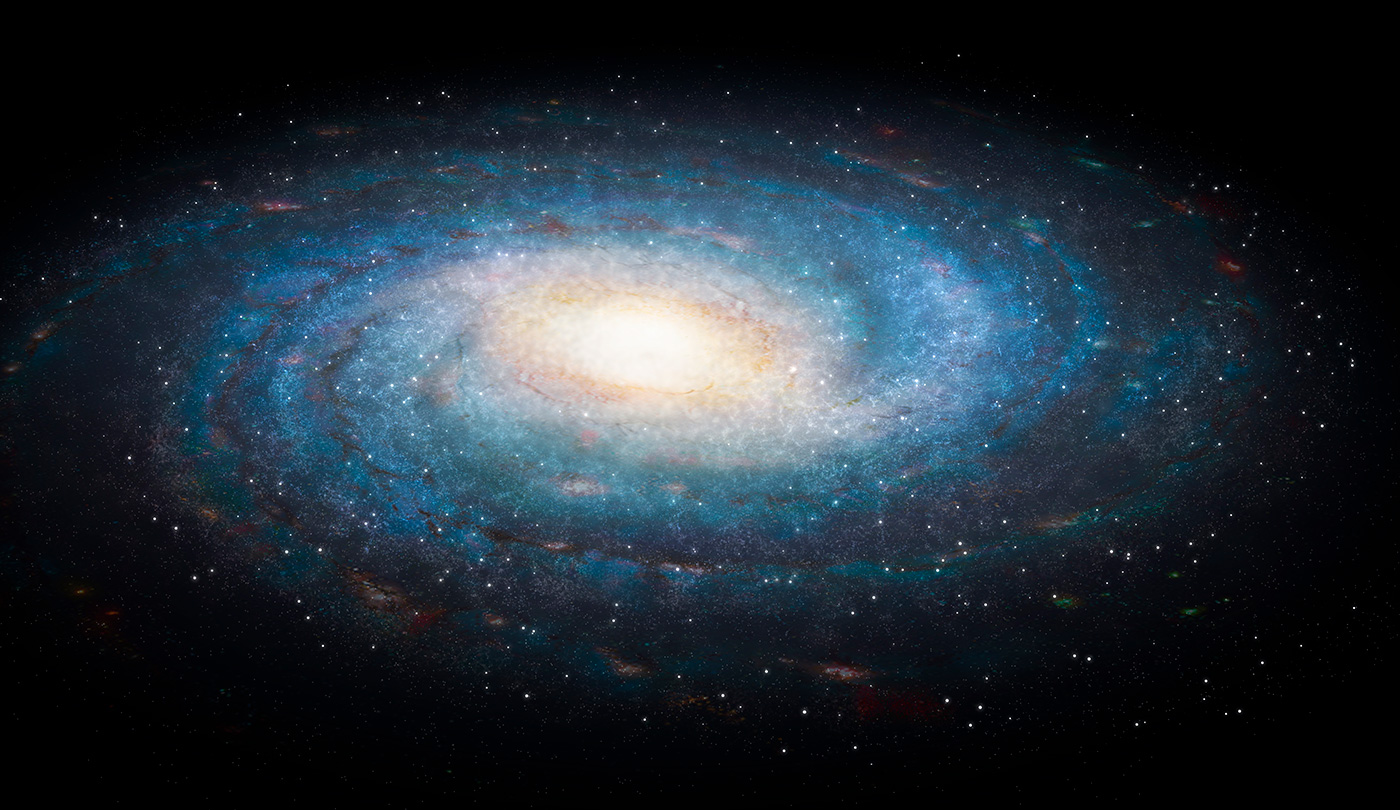

This galaxy was formed about 10 billion years ago from a huge cloud of gas and dust and contains about 500 billion stars.
Spatial Distances:
Distances in space are too large to be measured in miles or kilometers. Therefore, astronomers use light years to measure distances.
A light year is the distance that light travels through space in one year, which is approximately 6 trillion miles or 9.46 trillion kilometers.
The length of our galaxy is 100,000 light years and it takes 300,000 years for a radio message from Earth to reach its center.
The Closest Galaxies To The Milky Way:
The stars are not randomly scattered throughout the universe, but form different groups.
Each galaxy is made up of billions of stars. Our solar system is only a small part of the Milky Way. The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is the Small Magellanic Cloud and the Andromeda Galaxy.
Andromeda Galaxy:
Andromeda is similar to our galaxy, but a little bigger, which is the nearest large galaxy and is located at a distance of 2.9 million light years from us. In its center, there is a black hole that is millions of times denser than the sun.
More than 100 billion stars make up Andromeda.

A trillion stars that are moving towards us at a speed of 113 km per second and will collide with the Milky Way between 3 and 5 billion years from now.
This galaxy was first discovered by the Iranian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi in the fourth century of Hijri.
Large and Small Magellanic Clouds,the closest galaxies to the Milky Way:
The Milky Way has two small satellite galaxies called the Magellanic Clouds and named after Ferdinand Magellan.
Small Magellanic Cloud:
The Small Magellanic Cloud is an irregular type and is located at a distance of 190,000 light-years from the Earth. It contains many faint stars and has one or more X-rays. Its diameter is half the diameter of the Large Magellanic Cloud.
The speed of the Small Magellanic Cloud is less than the speed of the Large Magellanic Cloud and it reaches about 160 km per second, which can be seen in the Toucan constellation near the celestial south pole.

Large Magellanic Cloud:
This cloud is an irregular spiral and is located at a distance of 170 thousand light years. Its size is about a quarter of the Milky Way galaxy and it contains 15 billion stars and other space objects, and it can be seen in the constellation of the Golden Fish.
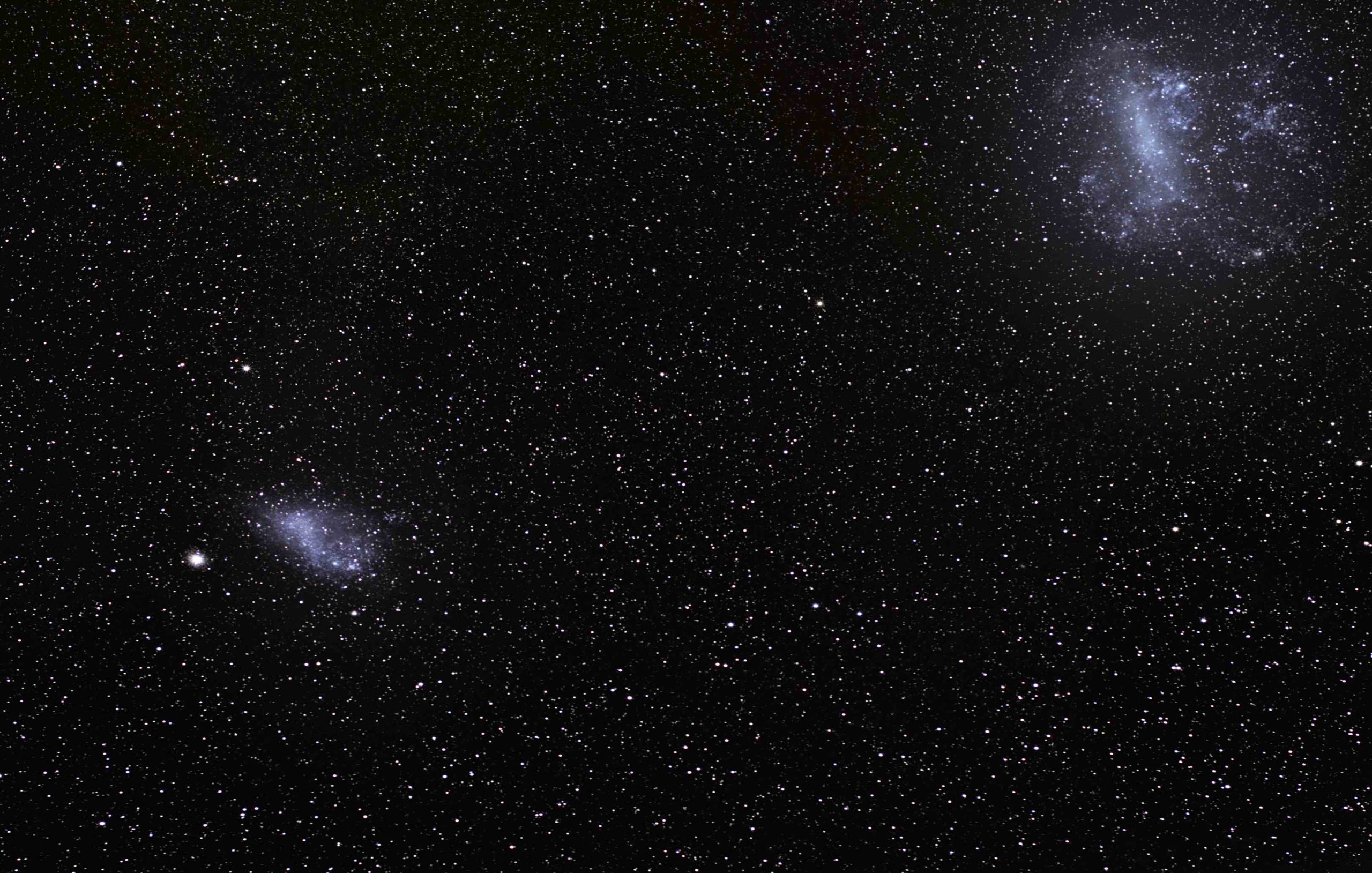

This cloud moves away from us at a speed of more than 250 kilometers per second.
The best time to see the Milky Way:
In the Northern Hemisphere:
the best time to see the Milky Way is between the months of July and October, and also in this hemisphere, the Milky Way looks magnificent in the dark nights of mid-winter.
In the Southern Hemisphere:
the best time to see it is between the months of October and December, and at this distance the Milky Way looks like a strip of milk that has been spilled across the sky.

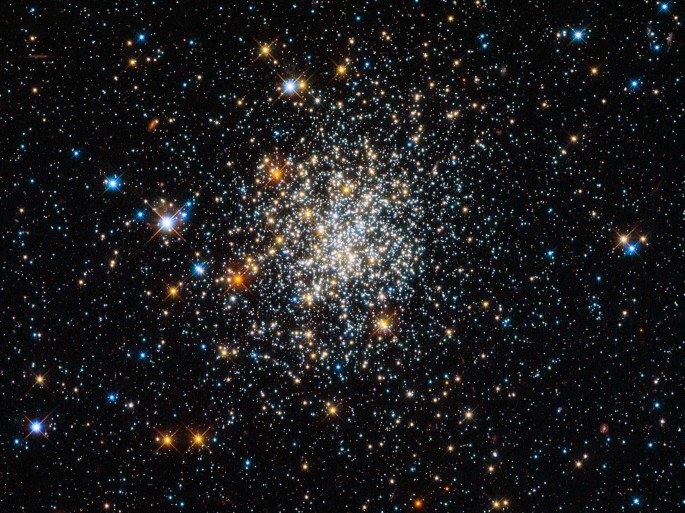
Clusters:
It seems that galaxies are located in groups in space, so far thousands of galaxy clusters have been found in all directions in space. Our local group, which consists of 30 galaxies, is only a small cluster of them.
An average cluster contains about 150 galaxies and extends over 15 million light-years.

Superclusters:
Superclusters are large groups of clusters that stretch and separate from each other during their movement.Our local group is part of a local supercluster that consists of many groups of galaxies.
They are so large that they are not gravitationally bound to each other.The existence of superclusters shows that our galaxies are not uniformly distributed.
The Most Famous Galaxies:
Cartwheel Galaxy:
The cartwheel galaxy is a giant galaxy and its width reaches 150 thousand light years. This galaxy resembles a cartwheel, which was created by another galaxy hitting it and this galaxy sinking into the cartwheel.
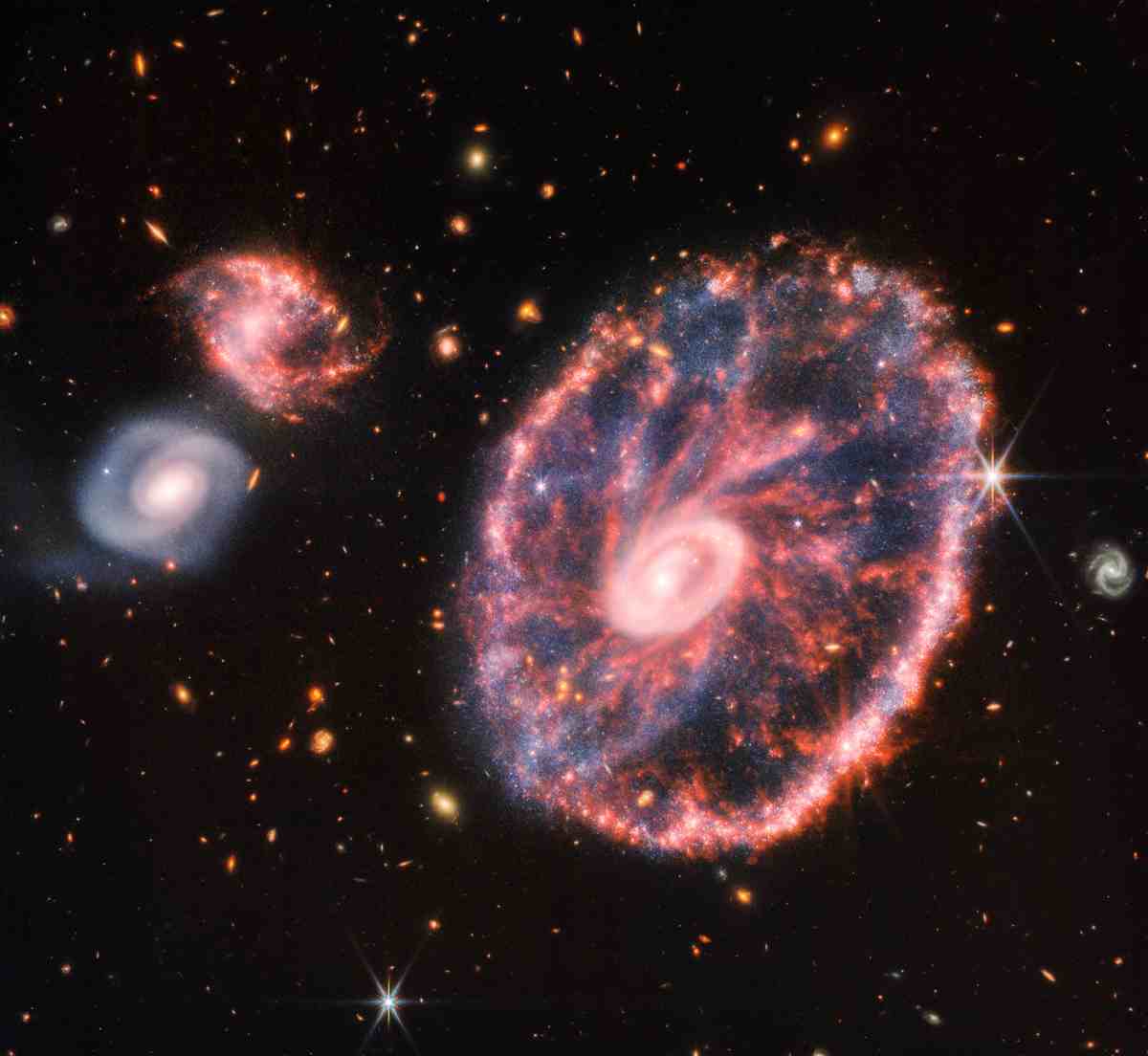

The outer ring is a very large ring of gas and dust that has expanded outward from the ring after the collision.
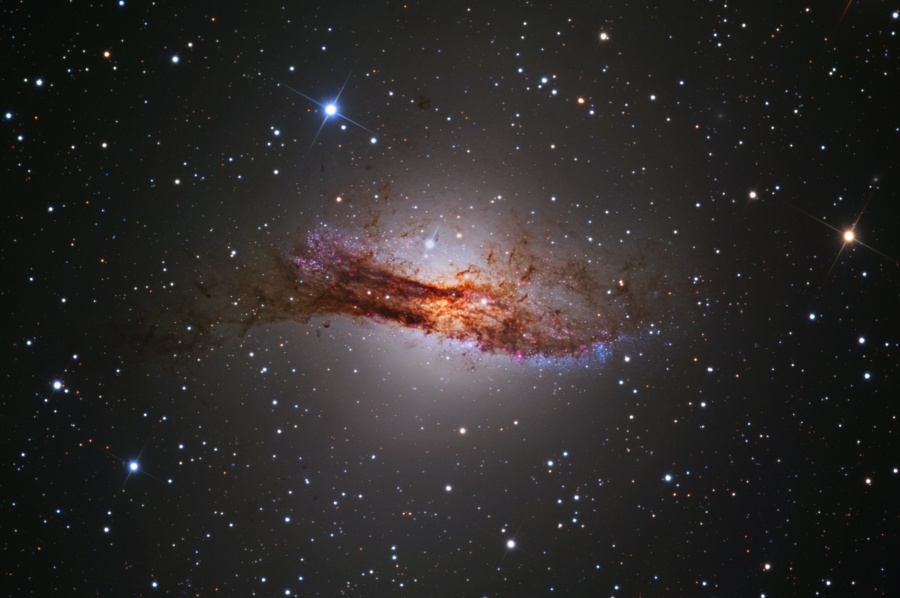
Centaurus A Galaxy:
It is one of the brightest and largest known galaxies and has almost 3 times as many stars as our galaxy and is an elliptical galaxy.
Scientists believe that huge explosions of millions of stars are taking place in the center of this galaxy, which are throwing out hot clouds of gas.

Important Point:
Galaxies never move in space, but according to Einstein’s theory of relativity, only the fabric of space expands and the galaxies are only mounted on this fabric. This expansion has no center and all points of space move away from each other.
What is a pseudo star?
It seems that quasi-stars, which are also called quasars, are the active nuclei of distant galaxies.Quasi-stars are considered the brightest, fastest and most distant known objects in the world.
Although the quasi stars are only the size of the solar system, the light of some of them travels a distance of about 10 billion light years to reach us, and in order to be able to detect such distant objects, we need a lot of light radiation.
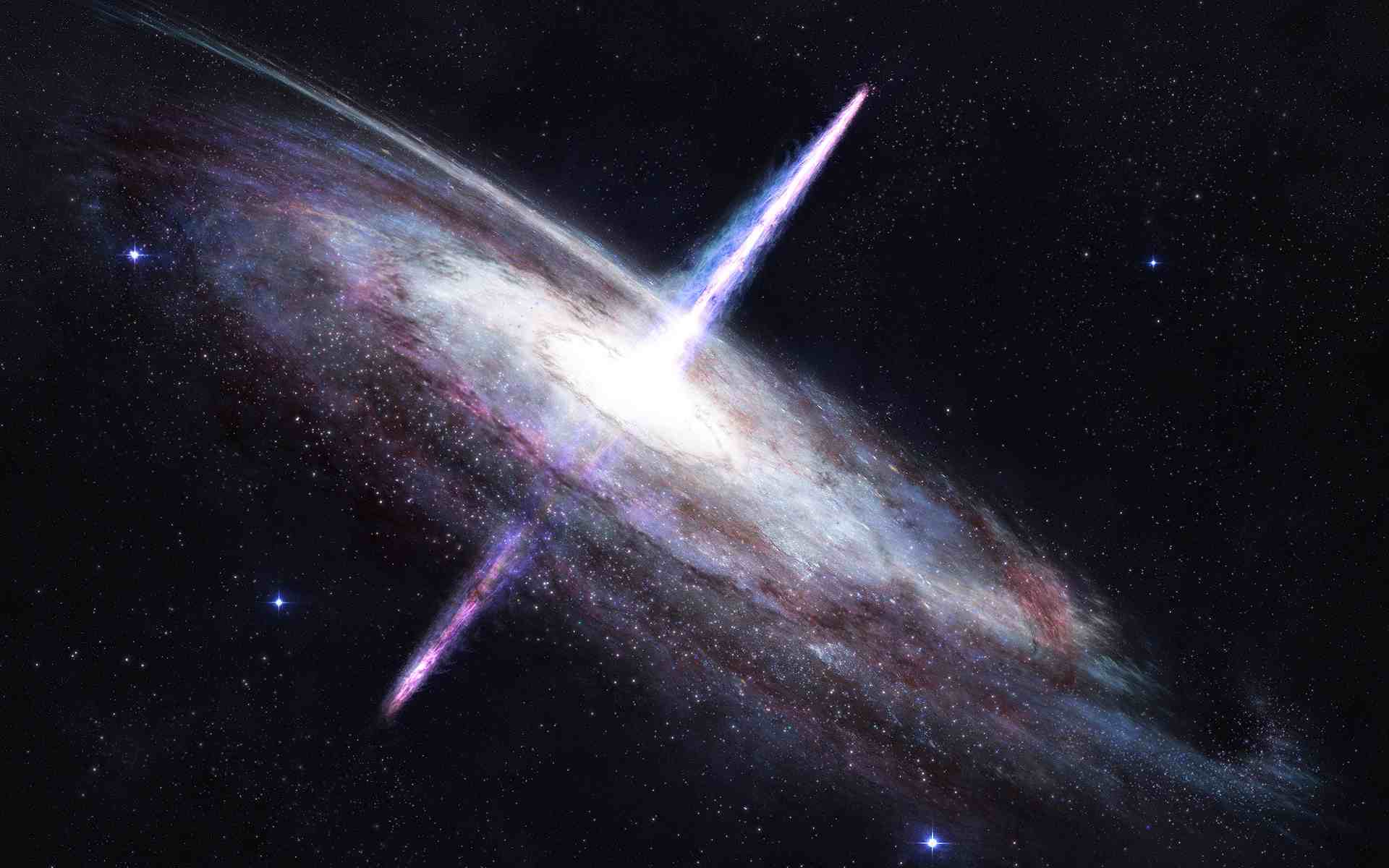

The energy radiation of some quasi-stars is about 100 times the radiation of massive galaxies. Quasi-stars are considered active nuclei belonging to young galaxies.
What do you know about radio galaxies?
All galaxies produce visible radio waves. The radio energy of these types of galaxies is much denser than ordinary galaxies. This energy radiates from two very large pieces or huge clouds of particles moving away from the galaxies.
Only one out of every million stars is a radio galaxy.

